
Spectroscopic analysis has shown that in the solar system, the planets of Venus and Mars have atmospheres very rich in carbon dioxide, both with atmospheres of over 95%. The decay of all organic materials produces carbon dioxide very slowly, and Earth ’s atmosphere contains a small amount of the gas (about 0.033%). English chemist John Dalton (1766 –1844) guessed in 1803 that the molecule contains one carbon atom and two oxygen atoms (CO 2) this was later proved to be true. Since these early discoveries, chemists have learned much more about carbon dioxide. In the 1770s, Dutch physiologist Jan Ingen-Housz (1730 –1799) established the principles of photosynthesis that helped explain the age-old superstition that plants purify air during the day and poison it at night.
#Carbon dioxide chemical formula series#
It uses up carbon dioxide and releases oxygen in a complex series of reactions that also require sunlight and chlorophyll (the green substance that gives plants their color). This energy-storing process, called photosynthesis, is essentially the reverse of respiration. However, plants also have the unique ability to store energy in the form of carbohydrates, the human body ’s primary source of food. Like animals, plants breathe, using up oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide. Around the same time, chemists began drawing the connection between carbon dioxide and plant life. In 1783, French mathematician, Pierre Simon de Laplace (1749 –1827) used a guinea pig to demonstrate quantitatively that oxygen from the air is used to burn carbon stored in the body and produce carbon dioxide in exhaled breath. The early study of carbon dioxide also gave rise to the expression to be a guinea pig, meaning to subject oneself to an experiment. In addition to supplying bubbles and zest, the gas acts as a preservative. Carbon dioxide is still used today to make colas and other soft drinks. This was the first artificially carbonated water, known as soda water or seltzer. When Priestley dissolved the gas in water, he found that it created a refreshing drink with a slightly tart flavor. Priestley had duplicated Black ’s experiments using a gas produced by fermenting grain and showed that it had the same properties as Black ’s fixed air, or carbon dioxide. The first practical use for carbon dioxide was invented by English chemist Joseph Priestley (1733 –1804) in the mid-1700s. As a result, scientists began to realize that gases must be weighed and accounted for in the analysis of chemical compounds, just like solids and liquids. The pioneering work of van Helmont and Black soon led to the discovery of other gases by English chemist and physicist Henry Cavendish (1731 –1810), French chemist Antoine-Laurent Lavoisier (1743 –1794), Swedish chemist Carl Wilhelm Scheele (1742 –1786), and other chemists. Black also identified carbon dioxide in exhaled breath, determined that the gas is heavier than air, and characterized its chemical behavior as that of a weak acid. Then in 1756, Scottish chemist Joseph Black (1728 –1799) proved that carbon dioxide, which he called fixed air, is present in the atmosphere and that it combines with other chemicals to form new compounds. For example, they discovered that a candle flame will eventually be extinguished when enclosed in a jar with a limited supply of air, as will the life of a bird or small animal.
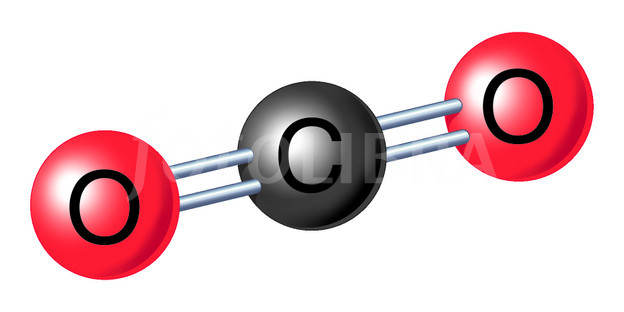
Before long, other scientists began to notice similarities between the processes of respiration and combustion, both of which used up and gave off carbon dioxide. He also recognized that carbon dioxide was produced by the fermentation of wine and from other natural processes. Van Helmont is credited with its discovery.
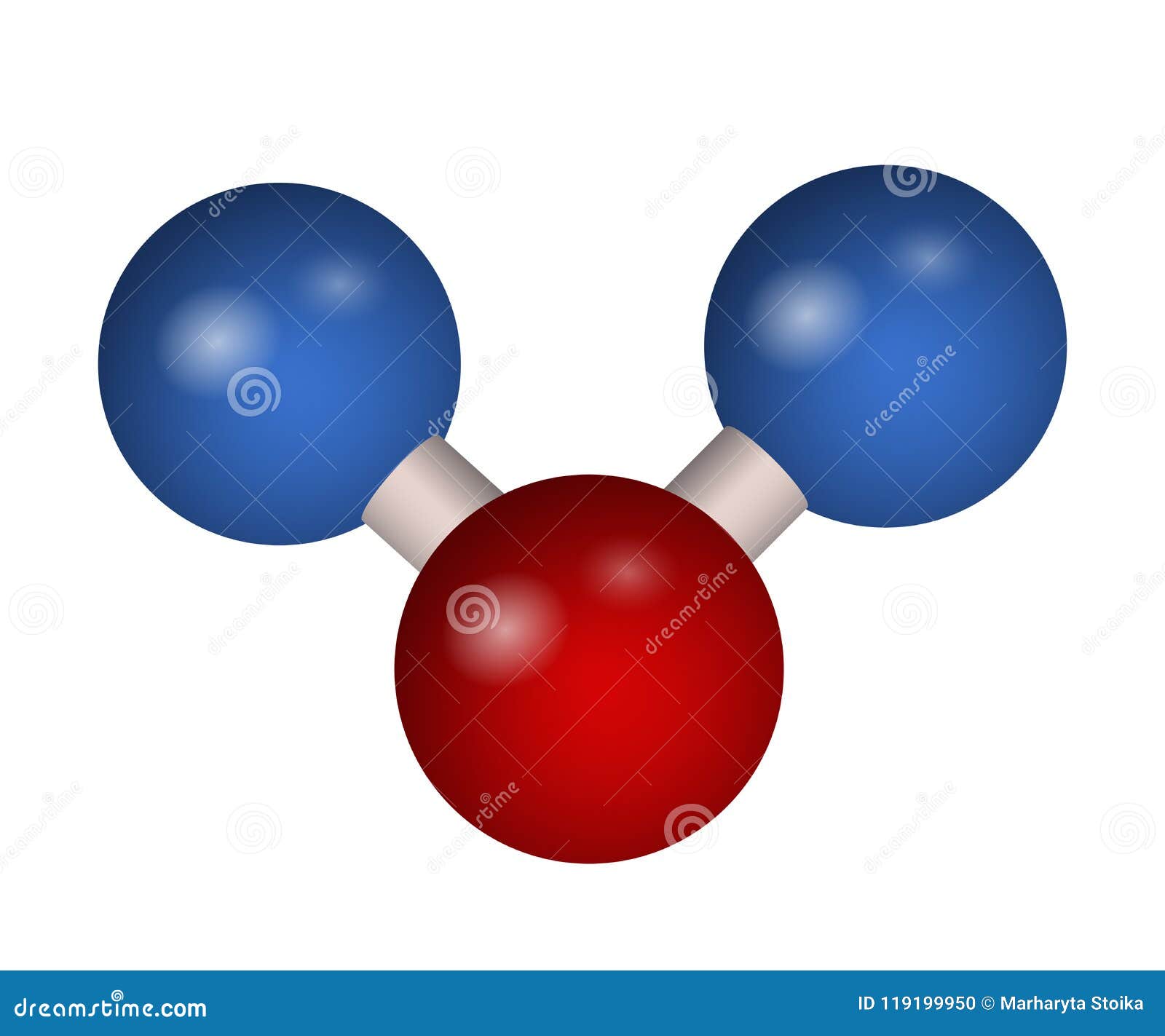
Today, this gas is known as carbon dioxide. Van Helmont coined the term gas to describe these vapors and collected the gas given off by burning wood, calling it gas sylvestre. Early scientists were able to observe the effects of carbon dioxide long before they knew exactly what it was.Īround 1630, Flemish scientist Jan van Helmont (1580 –1644) discovered that certain vapors differed from air, which at the time was thought to be a single substance or element. When humans breathe air or when wood and other fuels are burned, carbon dioxide is released when plants store energy in the form of food, they use up carbon dioxide. Carbon dioxide was the first gas to be distinguished from ordinary air, perhaps because it is so intimately connected with the cycles of plant and animal life. Sometimes called carbonic acid gas, its molecular makeup consists of one atom of carbon (C) attached to two atoms of oxygen (O): CO 2. Carbon dioxide is a heavy, odorless, colorless, faintly acid-tasting, and non-flammable gas (at room temperature) that is released during respiration, combustion, and by the decomposition of organic substances, which is then mostly absorbed from the air by plants in the process called photosynthesis.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
